中国组织工程研究 ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (44): 7675-7680.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.44.003
• 肾移植 kidney transplantation • 上一篇 下一篇
肾移植受者移植前免疫细胞亚群的检测及意义
黎东伟,刘龙山,费继光,王长希
- 中山大学附属第一医院器官移植中心,广东省广州市 510080
Detection of immune cell subsets in renal allograft recipients before operation and its significance
Li Dong-wei, Liu Long-shan, Fei Ji-guang, Wang Chang-xi
- Department of Transplantation, the First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510080, Guangdong Province, China
摘要:
背景:对肾移植受者免疫细胞的研究一直是移植外科的研究热点,但国内外缺少对肾移植受者术前全面、系统的免疫检测研究。
目的:探讨肾移植受者术前免疫细胞亚群的比例分布。
方法:纳入准备接受初次活体肾移植受者共15例作实验组;以18-40岁健康志愿者15人作对照组,分别抽取外周静脉血进行流式细胞检测。
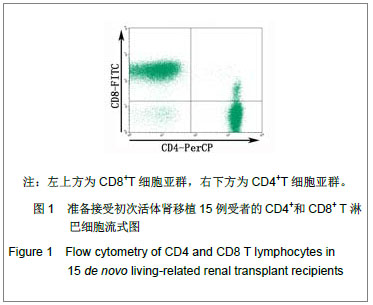
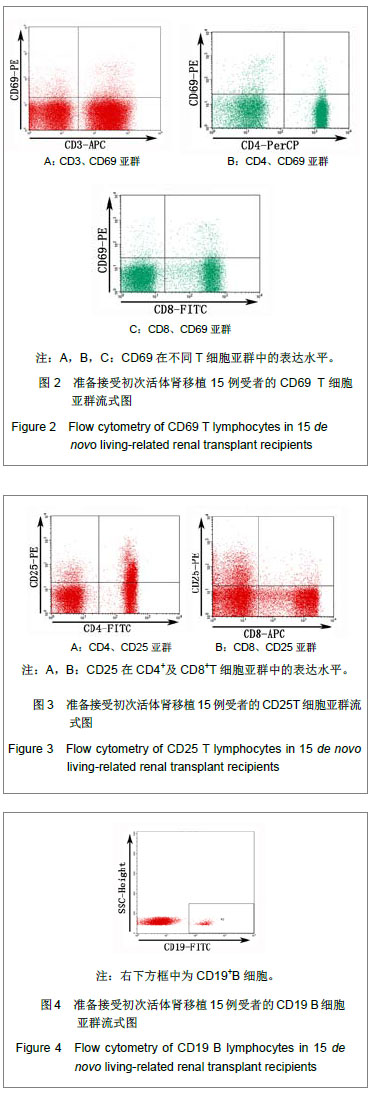
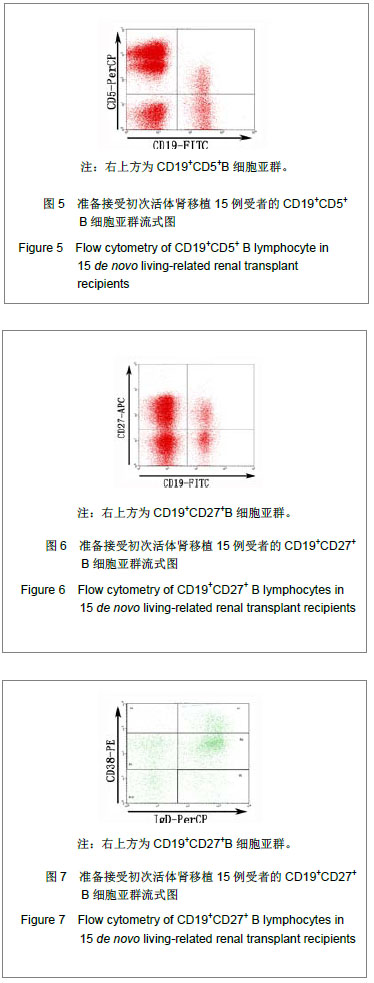
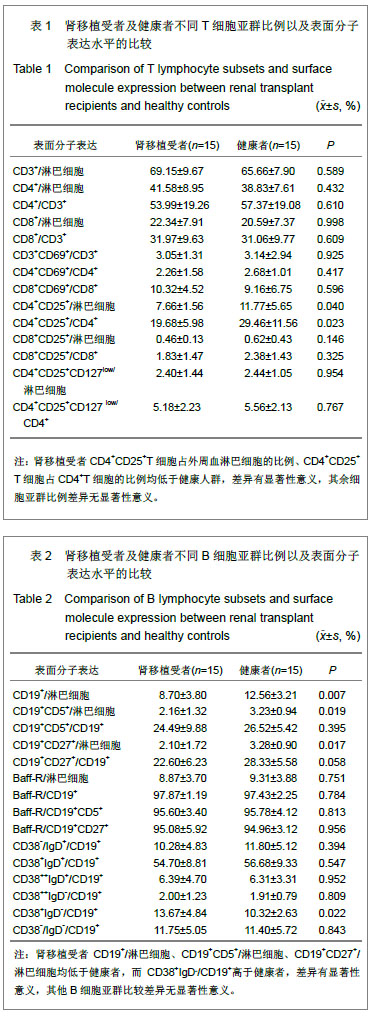
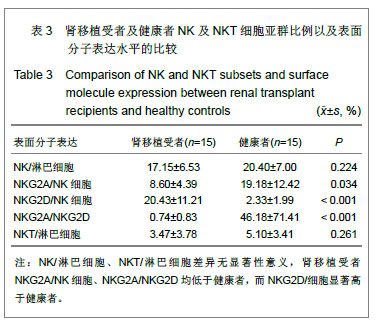
结果与结论:T细胞亚群:肾移植受者CD4+CD25+T细胞占外周血淋巴细胞的比例、CD4+CD25+T细胞占CD4+T细胞的比例均低于健康人群,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),其余细胞亚群比例差异无显著性意义。B细胞亚群:肾移植受者CD19+/淋巴细胞、CD19+CD5+/淋巴细胞、CD19+CD27+/淋巴细胞均低于健康者,而CD38+IgD-/CD19+高于健康者,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),其他B细胞亚群比较差异无显著性意义。NK及NKT细胞亚群的比较:肾移植受者NKG2A/NK细胞、NKG2A/NKG2D均低于健康者、而NKG2D/细胞显著高于健康者(P < 0.05),NK/淋巴细胞、NKT/淋巴细胞差异无显著性意义。说明肾移植受者移植前进行免疫细胞亚群流式分析,可以了解受者移植前免疫状态,对移植后免疫监测起基础对照作用。
中图分类号:

.jpg)